Your cart is empty.
Go shop.
CBD Cannabis vs CBD Hemp
As the popularity of Cannabidiol increases around the world, and the legality of consumption continues to evolve, numerous new products...
Thank you!
We'll get back to you as soon as possible.
Your cart is empty.
Go shop.


The uniqueness of the cannabinoid CBD as a natural pain reliever for a variety of medical conditions.
The debilitating nature of chronic pain can permeate diverse facets of social life. Daily activities like showering, going to work, or spending time with loved ones can be profoundly impacted by constant, gnawing presence of pain. Recent estimates suggest that as many as one in every five adults around the world lives with pain, with the prevalence increasing with age. In the US alone, about 50.2 million adults (20.5% of the population) reported pain on most days or every day.
For many individuals, the desire to live a life free of pain can be compromised by medications that can harbor serious unwanted side effects, including dependence. A general trend towards a holistic, balanced lifestyle has seen concerted efforts made to find natural compounds that can ease chronic pain. Among the known alternatives, CBD is starting to stand out as a natural analgesic that can be consumed using diverse delivery methods without cultivating dependence or causing serious side effects.
Unlike conventional analgesic agents, such as opioids, the body does not build tolerance to CBD so it can be used continuously without needing to increase the dose. CBD is also unique because it enacts pain relief via a range of biological processes in the body rather than through a singular mechanism. Finally, CBD has also been associated with anxiolytic and sleep-supporting properties: Anxiety and sleeplessness often go hand-in-hand with chronic pain. By elevating mood,enhancing sleep, and reducing pain, individuals living with chronic pain can experience relief on three distinct fronts.
Pain can be an abstract, intangible concept to wrap your head around. Pain doesn’t physically exist in the body, but is in fact a sensory and emotional experience: a signal sent by the nervous system that something is wrong. We can experience pain in a diverse range of ways, as a pricking, stinging, tingling, burning, or aching sensation.
The presence of pain can also trigger other symptoms such as an inability to sleep, the loss of appetite, irritability, anxiety, depression, and even increased blood pressure. Overall, pain can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life, triggering detrimental physical, emotional and mental changes.
To understand exactly what pain is and its effects on a person, it’s helpful to categorize it in different ways.
In the simplest terms, pain is often described based on its duration. It may be sharp (often associated with acute pain or an injury) or continuous (more frequently associated with chronic pain).
Beyond temporal categorizations of pain, it can also be conceptualized based on how it is experienced within the body, or its pathophysiological mechanism. The brain perceives and experiences pain differently based on which signals are being sent by the body.
Below are the two major types:
A. Nociceptive pain is “normal” pain, which originates in response to a stimulus that causes tissue damage. Examples of nociceptive pain could be burning your hand on a hot oven or cutting your foot on glass. Inflammatory pain is a type of nociceptive pain that results from the activation and sensitization of nociceptors by inflammatory mediators. When the body feels damage occurring, it calls these inflammatory cells into action. Inflammatory cells can be very helpful in the pain response as long as they “do their job” and evacuate the affected area once they are no longer required.
B. Neuropathic pain arises from damage to the peripheral nerve pathways, which doesn’t always occur in response to an external agent. Neuropathic pain can happen if your nervous system is damaged, or not working correctly. This kind of pain causes a shooting or burning feeling, or numbness and tingling.
Lastly, pain can also be defined by its location in the body’s tissue. Examples of the classification of pain according to the tissue involved include:
A. Myofascial pain
B. Joint pain
C. Bone pain
D. Visceral pain originating from an internal organ
E. Ischemic pain resulting from insufficient blood supply and insufficient oxygen to certain organ(s) or tissues.
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a major cannabinoid found in Cannabis sativa plants. Unlike THC, the other major cannabinoid found in cannabis, CBD is non-intoxicating, which means the user cannot get high after consuming it. CBD is, however, psychoactive, in the respect that can subtly alter mood. Studies of CBD suggest it is well-tolerated, safe, and has not been associated with any severe side effects.
Recent preclinical and clinical research probing the properties of CBD have uncovered that the cannabinoid boasts diverse beneficial therapeutic effects. CBD has been found to have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, antibacterial, antispasmodic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic, anxiolytic and antitumorigenic properties. In simpler terms, this impressive list of traits means that CBD can help to ease pain and inflammation, suppress nausea and seizures, protect brain and body cells, repel infection, inhibit the growth of tumors, and ease anxiety.
In addition, other studies have found that CBD may also help in the treatment of cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Its beneficial effects in suppressing seizures in rare forms of childhood epilepsy are already well-documented.

The body of research exploring the therapeutic applications of medical cannabis on illnesses characterized by pain is considerable. While the properties of cannabis are still being studied and not all of the pharmacological mechanisms of action have been fully elucidated, evidence for the plant’s pain-relieving properties are robust.
Over the past two years, many studies have been conducted exploring the effects of CBD on pain. These studies span in vitro research, preclinical studies on animals, and some clinical trials involving human participants. In addition, the anecdotal experiences of hundreds and thousands of patients and consumers who have tried CBD products offers naturalistic insights into the encouraging analgesic properties of this cannabinoid. Research demonstrates that CBD appears to be particularly proficient in treating pain arising as a result of inflammation, or nerve (neuropathic) pain.
CBD and neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is strongly linked to the glutamatergic system. Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate stimulates nerve cells, making it more likely that the chemical message (such as a message of pain) will move from nerve cell to nerve cell until the message is carried to the pain matrix of the brain. CBD suppresses the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate, thereby contributing to decreased chronic neuropathic pain symptoms.Teamed with other natural compounds such as magnesium, CBD can act as a natural form of neuropathic pain relief.
CBD and inflammatory pain
The anti-inflammatory mechanism of cannabidiol is unique. Unlike other conventional forms of anti-inflammatory pain relief that work by suppressing the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes (and increase the risk of digestive issues and heart trouble), CBD works via other mechanisms.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that CBD reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inhibits T-cell proliferation, induces T-cell apoptosis and reduces migration and adhesion of immune cells. Overall, this combined effort can help to significantly soothe the experience of inflammatory pain. Researchers have found that CBD may offer more powerful, pain relief than common anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen.
CBD appears to help ease chronic pain via a selection of biological mechanisms. Research to date suggests the cannabinoid can help suppress the sensation of pain as it passes through nerve messengers in the spine; desensitize a cation channel and reduce the sensations of pain, body heat and inflammation; modulates the body’s natural opioid receptors reducing the need for external opiates, and binds adenosine receptors that produce a significant anti-inflammatory response.
Let’s dive deeper into detail:
Reduction of pain sensation in the spine
Glycine is an excitatory nerve messenger that is involved in the transmission of pain sensation in the spine. CBD suppresses inflammatory and neuropathic pain by targeting α3 glycine receptors, inhibiting the sensation of pain as it passes through the spine on its way to the brain. The pain will be sent from the painful location via the receptors on the surface of the nerve cells, but it will not reach the brain because the CBD suppresses those receptors.
Activation of cation channels that are involved in the sensation of pain
Cannabidiol can desensitize a specific cation channel (the TRPV-1) which plays a role in the experience of pain, body heat and inflammation. The activation of this channel has been linked to pain relief, suppression of inflammatory processes and lowering of the body’s temperature.
Allosteric inhibition of opiate receptors:
Our body contains naturally-occurring opioid compounds such as endorphins and enkephalins, both of which can help to silence pain naturally. Many individuals with chronic pain are treated with external opioids, which can carry severe side effects. However, cannabidiol is an allosteric inhibitor of the body’s opioid receptors, meaning less opioids are needed for pain relief.
Attachment to adenosine receptors:
CBD can also bind to the body’s adenosine receptors, delivering a range of therapeutic benefits. One of the main results of this interaction is the production of a significant anti-inflammatory response. CBD appears to enhance adenosine signaling by inhibiting the uptake of the compound. As a consequence, the body’s inflammatory response is lowered, reducing the experience of pain and need for anti-inflammatory medication.
Activation of the 5-HT1A receptor:
Serotonin is a major neurotransmitter that is involved in regulating diverse bodily systems including nausea, appetite, anxiety, sleep, pain sensations and addiction. CBD interacts with the serotonergic 5-HT1A receptors. This activation may help to produce pain relief, uplift mood and ease anxiety.
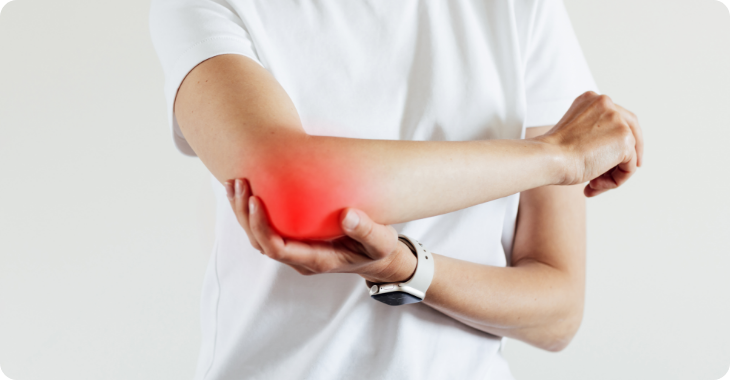
As the evidence for CBD’s pain-relieving properties increases, specific studies exploring its effects on diverse health conditions and disorders is also growing. Research shows us that CBD can beneficially ease a number of symptoms associated with chronic pain conditions, which we’ll outline in greater depth below.
CBD may also represent a powerful natural supplement for older people living with disorders that cause discomfort, inflammation, or pain. Learn more about how CBD can soothe pain and support mobility, mood, sleep and cognitive function in seniors.
Arthritis
There are more than 100 different types of arthritis and related conditions. All of these disorders share the same predominant symptom of the swelling and tenderness of the joints. As the joints play a pivotal role in ease of movement and mobility, chronic joint pain limits movement, and can profoundly affect patients’ quality of life. Since cannabidiol suppresses inflammation, the pain associated with this inflammation is also diminished. In particular, a number of studies have been carried out exploring the effects of CBD on rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with results showing a marked improvement in the pain associated with inflammation. CBD can also help arthritis sufferers experience an improvement in sleep and anxiety, which also contribute to the diminishment of symptoms associated with chronic pain.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by pain and disrupted communication between the brain and body. The pain related to multiple sclerosis increases during the spasms (spasticity) experienced by those living with the disease. Cannabidiol has been found to reduce spasms in multiple sclerosis, thereby also reducing the pain these spasms can cause. In addition, CBD can also reduce fatigue and pain, further alleviating chronic pain in MS sufferers.
Headaches and migraines
An overwhelming number of headache and migraine sufferers have found that CBD can ease the chronic, ongoing pain associated with the disorder. In one study, chronic migraine sufferers, (those who experience 15 to 29 headache days over a 30-day period) saw a 33% reduction in their headache days when using CBD oil. CBD appears to ease migraines via its anti-inflammatory mechanisms and analgesic properties that ease neurological pain. It can also ease nausea provoked by migraines, thanks to its antiemetic effects.
Back pain
Back pain represents one of the most common sources of chronic pain across the globe. In studies conducted on mice suffering from vertebral degeneration, CBD treatment helped to reduce the pain associated with the affected vertebrae. In humans, vertebral pain (such as the pain associated with slipped discs) can lead to swelling, inflammation, heat, and continuous radiating pain that makes it hard to sit, stand, or even lie down. CBD can ease inflammation, thereby reducing the swelling and the pain. Transdermal creams applied to the localized place of pain appear particularly effective in easing symptoms.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a disorder that particularly affects women. Common symptoms include joint pain, muscle pain, spinal pain, and even skin pain (a type of nerve pain known as tactile allodynia). The causes of these diverse expressions of pain often can be traced back to severe inflammation. CBD can reduce inflammation and nerve pain, and may also help to ease other chronic-pain related symptoms associated with the disorder such as irregular sleep, anxiety, depression and fatigue.
Digestive pain
Finally, CBD has also been shown to help treat inflammatory symptoms arising in the gut. Diverse disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn’s disease often seen sufferers experience digestive discomfort and abdominal pain. CBD has been found to be effective against many inflammatory symptoms experienced in the gut, by suppressing the release of interleukin cytokines and chemokines and increasing the production of T-regulatory cells, among other mechanisms. Studies and anecdotal reports suggest that oral CBD can improve symptoms in Crohn’s sufferers, and ease pain among those living with IBS.
CBD may help relieve the symptoms of several types of pain. Understanding the source and nature of your pain experience is vital to ascertaining whether CBD may help or not.
Ask yourself the following questions:
Being aware of the specificities of your pain experience can help you determine whether CBD may help ease your symptoms. Talking to a doctor experienced in cannabis medicine and chronic pain is also critical. With the right delivery method, dosage, and treatment plan, CBD can be a helpful alternative to managing chronic pain symptoms.
If you’re wondering which CBD product may best suit your needs, take the Kiara Health Quiz. While we cannot provide medical advice or diagnose your condition, we can provide you with support to find the product that will best address your concerns.
If you’d like to learn more about CBD and its chronic pain-relieving properties, we recommend the following scholarly articles.
Although many consumers report immediate pain relief, CBD does not work like a painkiller that binds to one or two target proteins (receptors) in the human body. CBD acts on about 60 target proteins in the body but it does not bind to any of them completely. Therefore, the effect of CBD on pain usually ranges from 4 hours to 5 days, depending on the intensity of the pain, the dose you take and the quality of the product. The advantage of CBD is that once you find the right dose, your body almost never develops a tolerance to CBD, so you won’t need to increase the dose.
Finding the right dose to solve pain problems consists of several factors: the intensity of the pain, body weight, age, general state of health, sports lifestyle, proper nutrition and more. Since each person has an endocannabinoid system that reacts to external cannabinoids in a different way – finding the appropriate dose is completely individual. We recommend starting with taking two drops a day for two or three days, then increasing to three drops for two days and so on – until the point where the pain relief is obvious. After reaching this point there is no need to increase the dose.
CBD can be consumed in a variety of ways and in a selection of products. CBD oil is considered a way in which the absorption of the active substance is fast, the utilization of the active substance by the body is considered very effective when taking CBD in the form of oil and most importantly – it is possible to accurately measure how many mg of CBD per day makes you feel pain relief. Taking CBD by ingestion through capsules or food enriched with CBD is a way in which the absorption of the active substance is slower, but in this way there is maximum utilization of the active substance. Taking CBD by vaping is considered particularly suitable for relieving flare-ups of pain and allows for mobility and accessibility during the day in case of an “emergency” Ointments and creams for applying to the skin are also considered an excellent way to relieve joint pain, muscle pain, and more.
We recommend taking CBD regularly, especially for people with chronic (persistent) pain. It takes between 36 and 72 hours for CBD to be completely cleared from the body, so even if you forgot to take your daily dose – usually the body will use CBD molecules that are still circulating in the bloodstream. There are people who for various reasons choose to take CBD only before an acute attack and it works for them very well as well. The The decision and introduction to CBD is all up to you. We will be happy to help and advise you in the process.
We recommend taking the CBD in the morning, after brushing your teeth and not drinking coffee for about 20 minutes before and after taking it. You can drink water to wash away the taste, but it is better to let the oil absorb itself. But it is not binding at all. There are people who have decided to take their daily dose at any other time of the day and that is totally possible if it works for them.
The daily dose can be spread throughout the day and night. If you take this approach make sure you track the patterns of symptom relief and the amount of CBD you consume.
As part of the safety trials for FDA approval conducted for a CBD-based medicine called “Epidiolex”, doses of 600-1200 mg of pure CBD per day were given to children suffering from a rare epileptic syndrome called Derva syndrome. At a dose of 600 mg per day, no significant side effects were observed and no liver toxicity developed, indicating an “overdose” condition.
An expert committee on behalf of the World Health Organization (WHO) for the control of narcotic substances, which in 2018 engaged in formulating an opinion regarding the medical properties of the cannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol), published its recommendations report under the title: CBD is a substance with extensive and significant medical potential. The report presented by the expert committee officially states that: “No potential harm or addiction has been proven as a result of using CBD. In studies of experimental models for addiction, it was discovered that CBD°has no addictive effect in a model for distinguishing between addictive drugs in animals, it was discovered that CBD fails to be used as a substitute for THC and as mentioned, in light of its widespread use by patients around the world, it can be determined that people do not develop any dependence on CBD And it cannot be used or abused.
As the popularity of Cannabidiol increases around the world, and the legality of consumption continues to evolve, numerous new products...
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of numerous cannabinoids, or chemical compounds, found in the cannabis plant...
Our skin, or dermis, is the biggest organ in the body. It is considered our defined border and the shield of our immune system...
The cannabis plant, one of the most researched plants in the world due to its rich and growing medical history, contains over 400 natural compounds...