Your cart is empty.
Go shop.
CBD Cannabis vs CBD Hemp
As the popularity of Cannabidiol increases around the world, and the legality of consumption continues to evolve, numerous new products...
Thank you!
We'll get back to you as soon as possible.
Your cart is empty.
Go shop.


A comprehensive guide from Kiara Naturals
The cannabis plant, one of the most researched plants in the world due to its rich and growing medical history, contains over 400 natural compounds. These including cannabinoids, active chemical compounds that are responsible for its many medicinal properties. Cannabidiol (CBD) is the second most abundant cannabinoid in the cannabis plant after tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the cannabinoid responsible for producing a ‘high’ sensation.
CBD offers a diverse range of healing benefits — without the psychoactive effect of THC. It is known for the treatment numerous medical conditions, including inflammation, autism, epilepsy, chronic pain, stress and ADD/ADHD, among others.
The fact that CBD has no psychoactive effects, and carries side effects that are often milder and more tolerable than those that accompany conventional synthetic medications, makes it an increasingly desirable treatment among many patients.
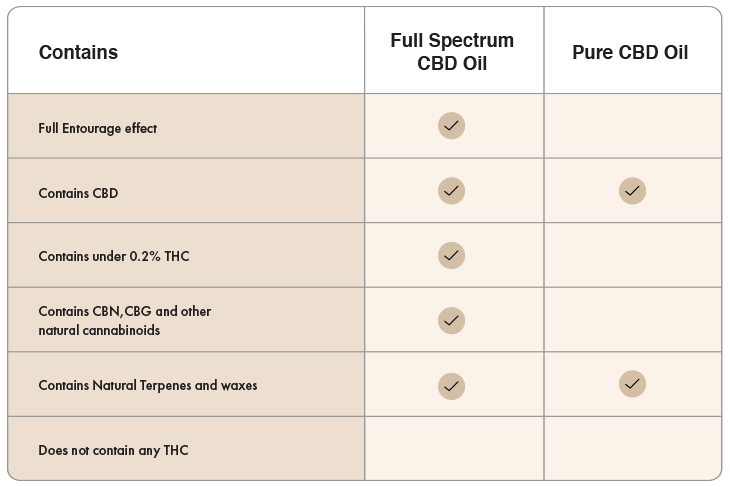
Cannabidiol can be extracted from either hemp or marijuana, two different varieties of the cannabis plant. Hemp is the term for cannabis plants containing less than 0.3 percent THC, whereas marijuana refers to cannabis plants containing more than 0.3 percent THC. All CBD products, no matter which variety of the cannabis plant they are extracted from, should include less than 0.3 percent THC and will not produce a psychoactive effect. However, most CBD products are derived from hemp plants due to their naturally low levels of THC and growing legality.
After the cannabis plant is cultivated and harvested, CBD can be extracted using a number of methods, each with its unique benefits and process.

Not only can CBD be extracted using different methods, it can also be made using different compounds of the cannabis plant, resulting in products with differing uses and benefits. The three compounds within the cannabis plant are cannabinoids (among them CBD and THC), terpenes, which affect the aroma of the plant and carry therapeutic effects, and flavonoids, which also produce therapeutic effects.
Cannabidiol products come with varying concentrations of CBD, with the recommended concentration depending on the person and condition being treated.
The proper dose of CBD ranges from 20-200 milligrams a day and depends on the person taking it, as every body responds uniquely. It is recommended to start with one drop under the tongue twice a day, and increase the dose as needed until relief is found.
When Cannabidiol is used in its various forms, it affects our bodies by interacting with our endocannabinoid system (ECS).
The endocannabinoid system is a complex system that is active in our bodies, whether or not we use cannabis. While research is still being done on how the ECS works, we know that it plays a role in maintaining your body’s homeostasis, or internal balance and stability. When something throws off your body’s homeostasis — such as injury or illness — the ECS helps your body return to normal.
Experts are not yet clear on precisely how CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system, but it is proven to enhance its effects. While the exact process is yet to be understood, research shows that CBD can help with inflammation, pain, sleep, and multiple other functions regulated by the ECS.
Numerous studies have been conducted over the past decades assessing the impact of CBD on a variety of conditions ranging from pain to anxiety. Research into CBD’s effects and ways of working is continuously growing, and leading to exciting findings related to physical, mental and emotional health.
Pain relief: The use of cannabidiol to treat chronic pain dates back thousands of years. Still today, pain relief is the most common reason for the use of medical cannabis in the US. CBD helps to regulate the activity of the nervous system, while blocking pain promoting agents in the brain, and stimulating the immune system to reduce inflammation.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6222489/
Skincare: When applied to the skin as an ointment, CBD can significantly reduce acne. One of the causes of acne is underlying inflammation, and the overproduction of an oily secretion produced by the skin, called sebum. Recent studies show CBD oil may help treat acne due to its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to reduce sebum production. In addition, CBD has been shown to relieve psoriasis and minimise the appearance of scarring.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4151231/
Focus: CBD effectively relieves many of the factors that impair our focus — pain, anxiety sleep — and can therefore naturally help boost our concentration. Research investigating additional effects of CBD on concentration is currently anecdotal, but results are promising. A 2017 study on adults with ADHD showed that a combination of CBD and THC led to the reduction of ADHD-related symptoms.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28576350/
Anxiety: CBD relieves stress and anxiety by positively invigorating neural regeneration and regulating the endocannabinoid system, which becomes deregulated during times of stress.
CBD also binds to serotonin receptors, specifically the 5-HT1A receptor which is responsible for anxiety disorders. A number of studies have shown that CBD oil is highly effective in treating anxiety, depression and stress in a variety of beneficial ways.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26341731/
Inflammation: CBD shows potential as a powerful anti-inflammatory without the side effects of synthetic medications. It reduces inflammation through several mechanisms of action, and represents an effective potential treatment for a range of conditions characterized by inflammation, including arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828614/
Cancer: CBD can be extremely beneficial in blocking the growth of tumors, and may also be beneficial in treating certain types of cancers triggered by chronic inflammation. In such instances, CBD can either directly inhibit tumor growth, or suppress inflammation and the growth of the blood vessels that help sustain the tumor. Furthermore, The National Cancer Institute lists CBD as a treatment for reducing common side effects of chemotherapy, including pain, vomiting, and lack of appetite.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6928757/
Sleep: Cannabidiol can help us get a better night’s sleep by alleviating some of the root causes of sleeplessness, such as pain and anxiety. However, CBD boasts additional benefits in treating sleep disorders because of its interaction with the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in the regulation of the circadian sleep–wake cycle — including the maintenance of healthy sleep. Pilot studies have shown promising results of the effects of CBD on sleep and fatigue.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5101100/
Recovery: The main role of CBD in recovery is reducing inflammation. While inflammation is integral to exercise-induced muscle damage repair, regeneration, and adaptation, excessive inflammation may contribute to prolonged muscle soreness and delayed functional recovery. Inflammation reduction is important for limiting the damage caused to the muscles, joints and nearby tissues. CBD offers to reduce inflammation and pain, lower tension, and quicken the recovery process of the body after an injury or an intense workout.
While cannabis is illegal in many parts of the world, the CBD derivative is legal in many countries when used for health and wellness purposes. CBD extractions are considered food supplements in most of the EU and the US. In other countries CBD is considered a pharmaceutical, sold only in pharmacies. In some countries it remains illegal.
Drug tests do not screen for CBD because it does not cause intoxicating effects, and is, in most places, not an illegal substance. However, people who use CBD could potentially fail a drug test if the CBD product contains traces of THC.
While CBD is unlikely to have an effect strong enough to impair your driving, you should assess your personal reaction to CBD before getting behind the wheel.
CBD does not produce the psychoactive effect felt when using THC.
Full spectrum CBD products contain 0.3% or less THC. Broad spectrum oils and CBD isolates do not contain any THC.
Dosage is a factor in determining whether or not CBD will make you drowsy. At low doses, it should not lead to drowsiness, but at higher doses it may. Every body reacts uniquely to cannabinoids, and you should assess your own personal reaction.
More research is needed to understand the full effects of CBD on appetite, as it seems to vary. Some studies show it leads to an increase in appetite, whereas others actually suggest it could promote weight loss.
In most countries in Europe and most states in the US, you can purchase hemp-derived CBD oil without a prescription. Make sure to check local state and country laws to determine the legality of CBD oil and other CBD products.
As the popularity of Cannabidiol increases around the world, and the legality of consumption continues to evolve, numerous new products...
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of numerous cannabinoids, or chemical compounds, found in the cannabis plant...
Our skin, or dermis, is the biggest organ in the body. It is considered our defined border and the shield of our immune system...
Vaping is the process of inhaling vapor produced by a device that heats up liquid or herbs...